Niantic tries its hand at sports with NBA All-World
Niantic, the company behind the mega-hit Pokémon GO, has reached an inflection point.
Whether because of pandemic fatigue or frustration over the limitations of today’s AR tech, the Google-spawned startup has struggled mightily to replicate the success of GO, which became one of the fastest-growing games in history shortly after it launched in July 2016. Niantic shut down Harry Potter: Wizards Unite, its first high-profile title after GO, just two years post-debut, while another tentpole project — Pikmin Bloom — has generated only a fraction of the downloads that GO attained over the same time frame.
Last June, Niantic laid off 8% of its staff — about 85 to 90 people — and canceled four of its projects, including a Transformers game that had already entered beta testing.
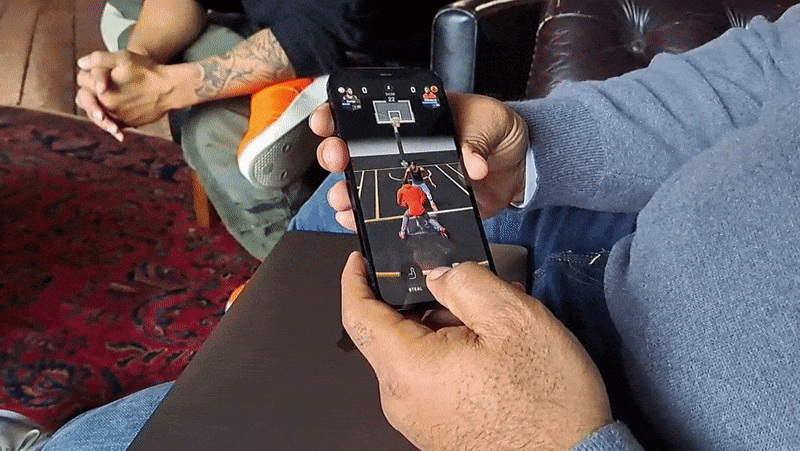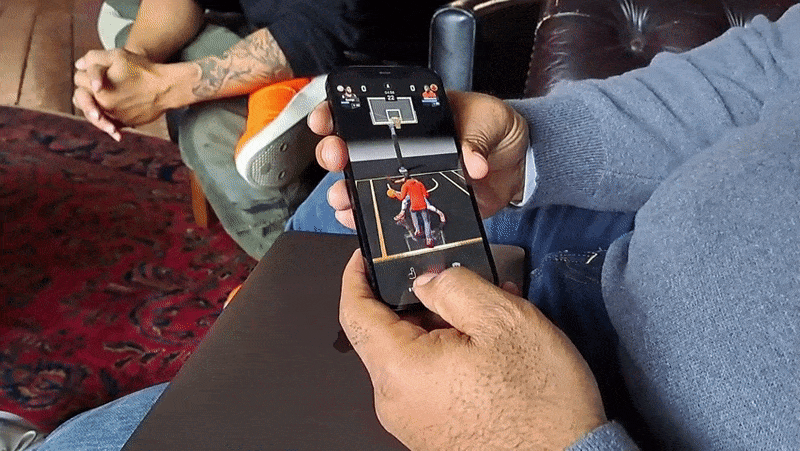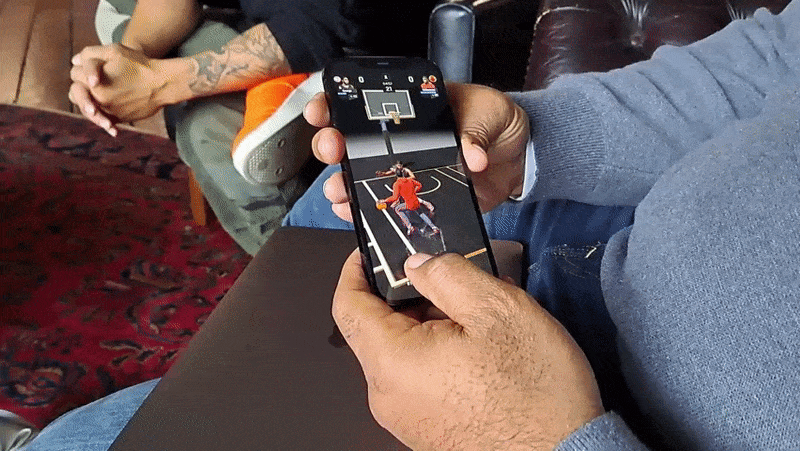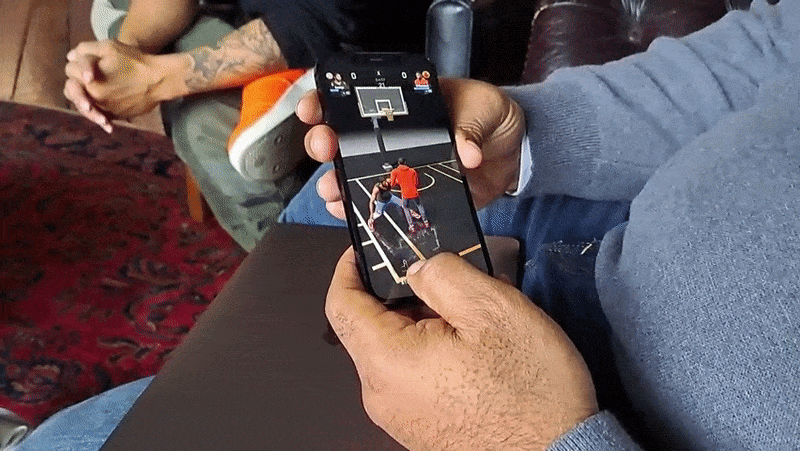
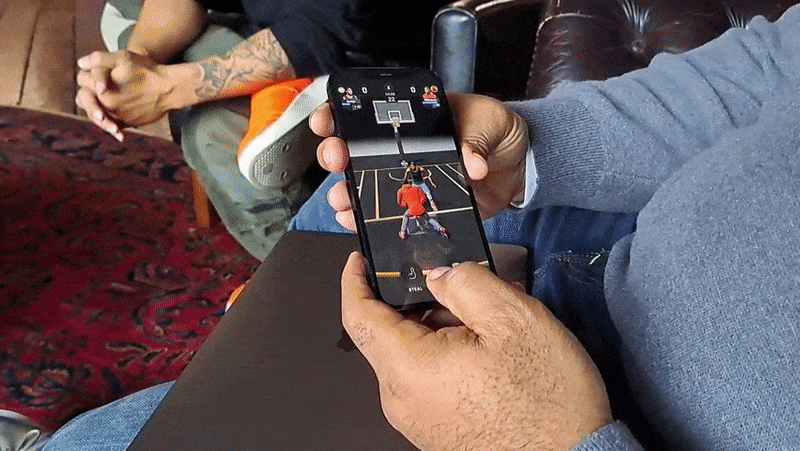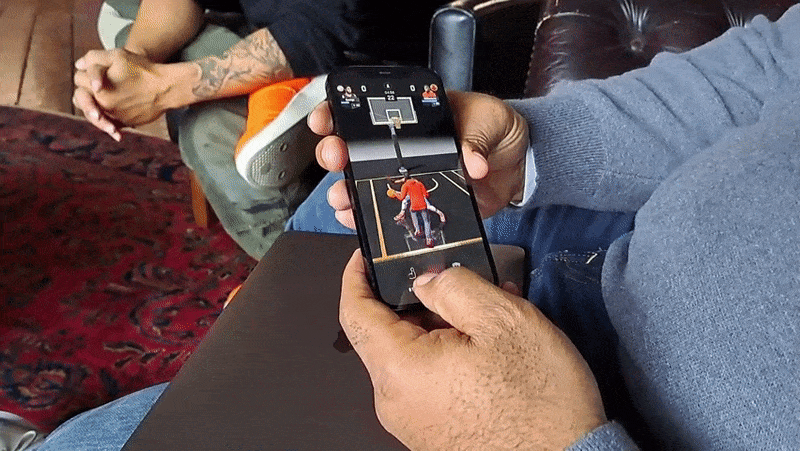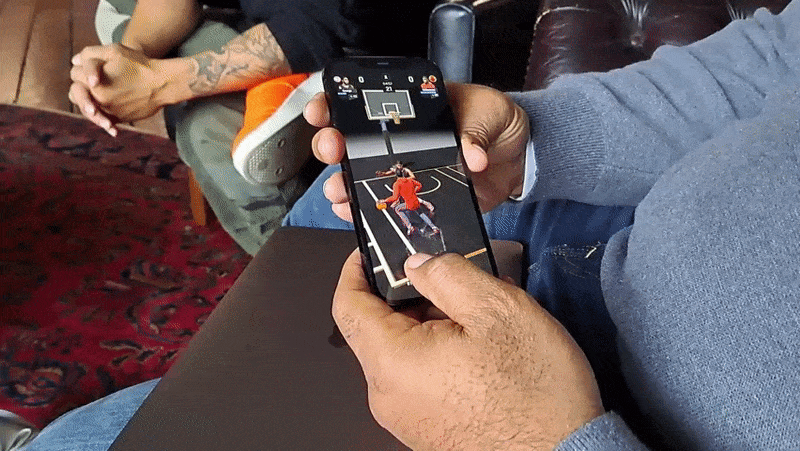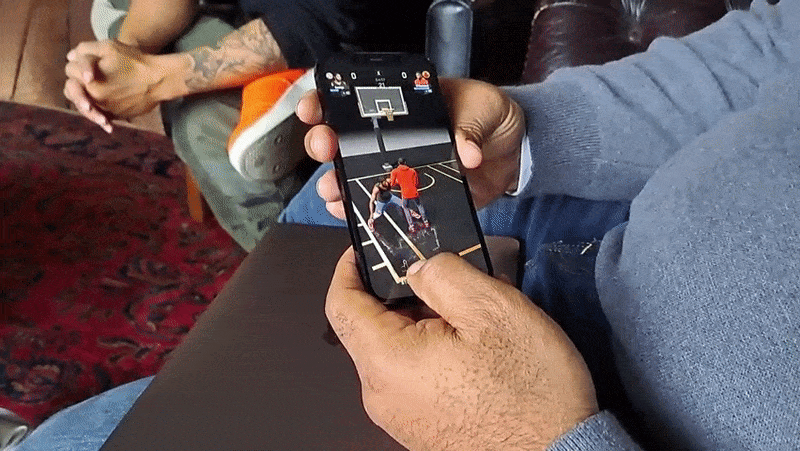
Needless to say, there’s a lot riding on NBA All-World, Niantic’s latest attempt to again achieve iOS and Android virality. Revealed last summer in a joint announcement with the NBA and National Basketball Players Association, All-World — which is visually quite similar to GO — is chock full of merchandise, nods to basketball culture, minigames and opportunities to meet avatars of real-world NBA players like Jordan Poole, Karl-Anthony Towns and Andrew Wiggins.
I’ll be the first to admit that I’m not All-World’s core demographic. The only team I’ve ever followed is the Cleveland Cavaliers, and that’s simply because I grew up near Cleveland (and, well, LeBron’s stardom didn’t hurt). Being that I’m not much of a sports person — my preferred type of game involves controllers and screens — I hadn’t given All-World much thought until Darrell Etherington, TechCrunch’s managing editor, assigned me to write a first impressions piece.
So I went in blind to my All-World demo, which took place on a gray and gloomy, rainy afternoon at the Compound near Red Hook in Brooklyn. The Compound, I was informed by the PR folks who arranged the affair, was founded by hip-hop DJ Set Free Richardson of AND1 fame. Neat. In any case, the loft-like space was nicely appointed, with checkerboard-patterned rugs, Picasso-esque prints and a pool table racked and ready for play.

Image Credits: Kyle Wiggers / TechCrunch
But I wasn’t there for pool. After arriving and pouring myself a cup of coffee, I plopped down on a thick leather couch next to Glenn Chin, head of global marketing at Niantic, and Marcus Matthews, a senior producer for All-World, to walk through All-World a day ahead of its release on the Play Store and App Store.
I started with the obvious question: why basketball, now, for Niantic? Why’d the studio choose this sport for its next AR venture? Answering candidly, Chin pointed out that licensing deals are far easier to strike with an international organization like the NBA as opposed to, say, disparate soccer confederations. But he and Matthews — who grew up playing basketball in Downtown Jacksonville, Florida — repeatedly emphasized basketball’s communal aspect, too, particularly in cities with public courts where kids and teens gather (so I’m told) to casually shoot some hoops.
In emphasizing social, the dev team behind All-World followed in the footsteps of GO, which — beyond Pokémon sheer brand strength — resonated because of the compelling mix of shared and competitive experiences it delivered. (Think gym battles with strangers and mad dashes for rare Pokémon.) It’s the fine-tuning of a familiar formula, albeit with a few twists and adaptations to meet the expectations of today’s game-playing audience.

Image Credits: Niantic
As with GO, All-World players can explore their own neighborhoods for collectibles, power-ups and other items of varying intruige. Exploring requires physically walking to a place — this is a Niantic game, after all — and navigating menus by tap- and swipe-based gestures. In-app, you’re represented by an avatar.
All-World is built on Niantic’s Lightship platform, which leverages the Unity game engine to power graphics and gameplay. Orlando-based HypGames co-developed the experience with Niantic; HypGames CEO Mike Taramykin served as VP and GM over EA’s Tiger Woods franchise until 2013.
On top of a real-world map of a player’s surroundings, All-World layers things like power-ups, challenges, gear, boosts and in-game currency. There wasn’t much near the Compound when Matthews demoed the game to me, but he managed to pick up some moolah that could be put toward apparel for his NBA player avatars.
A central mechanic in All-World is recruiting those players, who can then be “leveled up” to become the “rulers” of local basketball courts. (The game has over 100,000 courts at present.) Players can challenge each other to three-point shootouts and other timing-based minigames in recreations of real-world courts, which not only increase the level of a player’s recruits but also their overall team level.
The team level serves as a merit-based stand-in for real-world salary caps — the higher the level, the stronger the NBA players an All-World player can recruit.
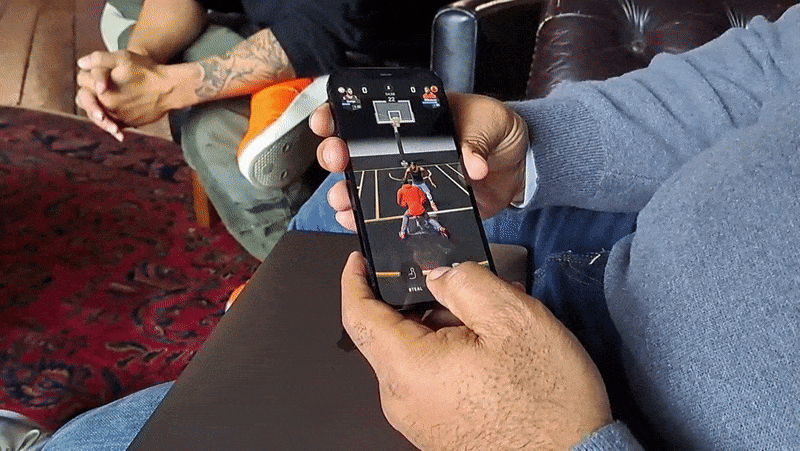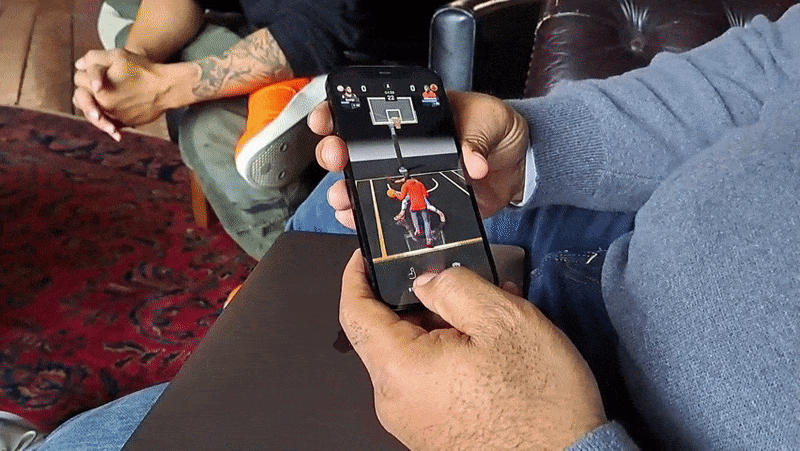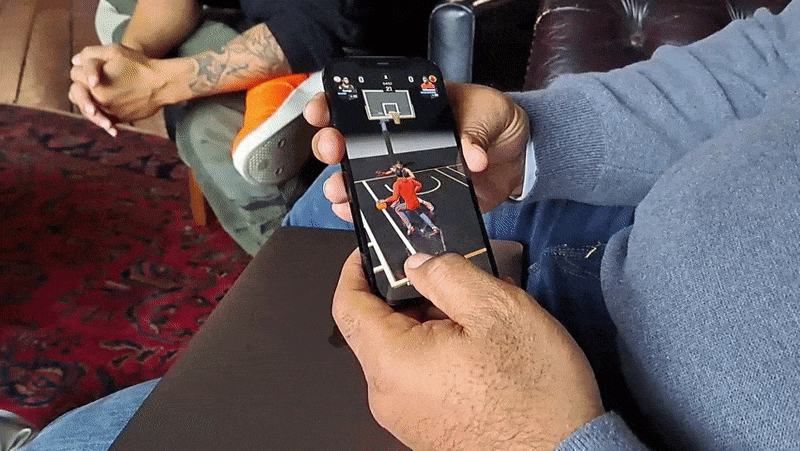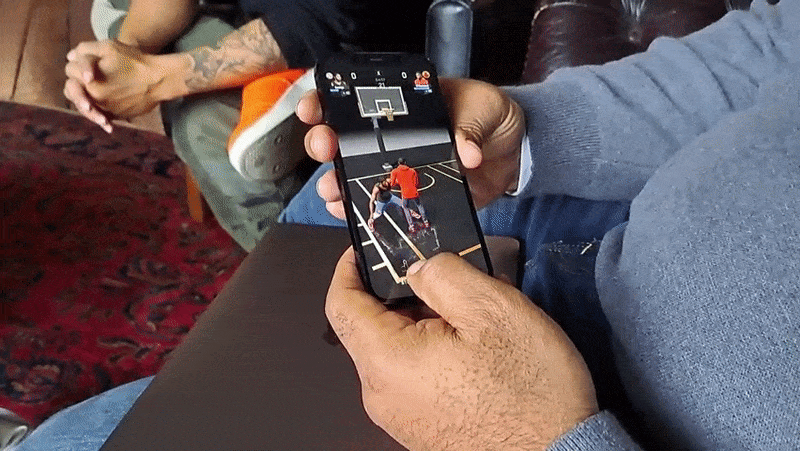
Image Credits: Kyle Wiggers / TechCrunch
Adjacent to this, All-World has a robust merchandising component. Players can search for “drops” of jerseys and more (a la Supreme) from brands such as Adidas and Nike that mirror real-world SKUs. Their in-game team members don this merch, some of which improves their game stats. Chin says that the plan is to work with additional brands to create and recreate accessories, balls, clothing and sneakers and even time drops with real-world product launches.
The merch mechanic was built to reflect — and respect — the basketball fan frenzy around collectibles, Chin and Matthews say. I don’t doubt that fact. But there’s an obvious profit motive, too. All-World might be free-to-play, but it certainly isn’t a charity.
As another case in point, Niantic also plans to make money by selling “boosts” for player stats like offense and defense, which improve performance in the minigames. Chin and Matthews don’t deny players who shell out can advance through certain aspects of All-World faster. But Matthews stressed that players don’t need to fork over cash if they play relatively often.

Image Credits: Niantic
That remains to be seen. I was only treated to glimpses of the game — which, unfortunately, experienced some freezing issues during the demo. (Matthews blamed the Compound building’s poor reception, which isn’t unlikely — it wasn’t good.) The bigger-picture question is whether All-World has staying power — and indeed, whether it can make enough noise to stand out in the ultra-crowded mobile market.
With All-World, Niantic is placing bets both on the strength of the NBA brand and the appeal of AR. As a sports ignoramus, I can’t speak on the former point. But on the latter, I wouldn’t write a eulogy for AR just yet. The tech’s just getting started, I’d argue — especially if rumors of an Apple headset someday come to pass.
If Niantic can keep All-World fresh and interesting with compelling AR-focused gameplay, it might just have a fighting chance. (My impression is that it’s a bit light on content at the moment, but to be fair, it’s early.) On the other hand, if All-World devolves into a pay-to-win collect-a-thon down the line, I can’t see it topping the download charts for very long — if ever.
As for what All-World’s success or failure might spell for Niantic, it wouldn’t tank or make the company necessarily. Niantic sells its Lightship platform to developers as a paid service. And GO is still going (pun intended) strong, with revenue estimated to be north of $1 billion. Besides, Niantic raised $300 million at a $9 billion valuation in November 2021 — more than doubling its valuation from 2018.
But after years in development, it’d no doubt be a disappointment for the studio — and for the NBA head honchos who evidently have faith in Niantic’s ability to spin viral magic.