OpenAI's new tool may help you identify text written by ChatGPT
OpenAI has released a tool to help you determine whether text was more likely written by a human or AI. However, the ChatGPT maker warns that its equivalent of Blade Runner’s Voight-Kampff test can also get it wrong.
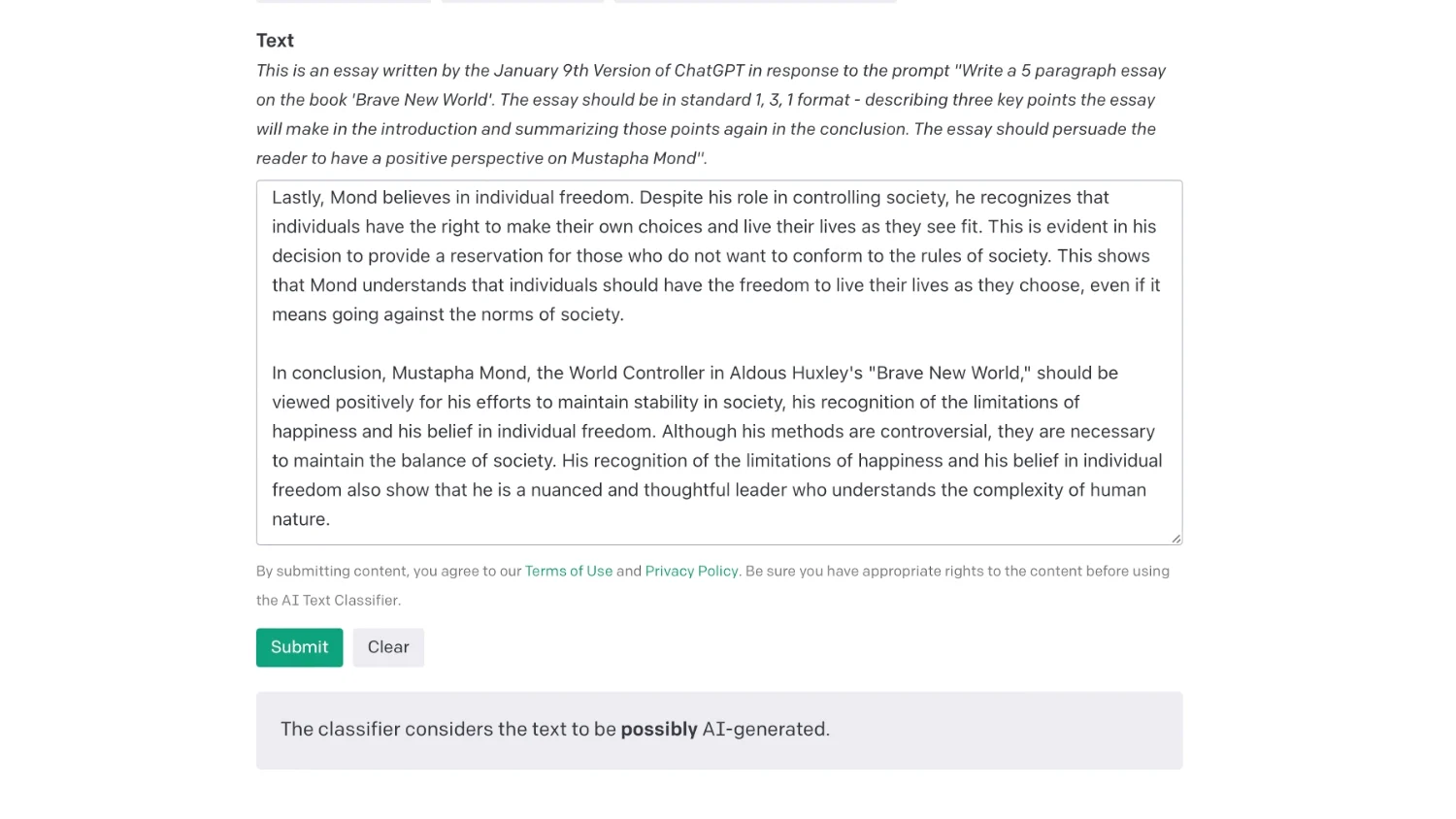
The tool includes a box where you can paste text that’s at least 1,000 characters long. It will then spit out a verdict, like “The classifier considers the text to be very unlikely AI-generated” or “The classifier considers the text to be possibly AI-generated.”
I tested it by prompting ChatGPT to write an essay about the migratory patterns of birds, which the detection tool then described as “possibly AI-generated.” Meanwhile, it rated several human-written articles as “very unlikely AI-generated.” So although the tool could raise false flags in either direction, my (tiny sample size) test suggests at least a degree of accuracy. Still, OpenAI cautions not to use the tool alone to determine content’s authenticity; it also works best with text of 1,000 words or longer.
The startup has faced pressure from educators after the November release of its ChatGPT tool, which produces AI-written content that can sometimes pass for human writing. The natural-language model can create essays in seconds based on simple text prompts — even passing a graduate business and law exam — while providing students with a tempting new cheating opportunity. As a result, New York public schools banned the bot from their WiFi networks and school devices.
While ChatGPT’s arrival has been a buzzed-about topic of late, even extending into media outlets eager to automate SEO-friendly articles, the bot is big business for OpenAI. The company reportedly secured a $10 billion investment earlier this month from Microsoft, which plans to integrate it into Bing and Office 365. OpenAI allegedly discussed selling shares at a $29 billion valuation late last year, which would make it one of the most valuable US startups.
Although ChatGPT is currently the best publicly available natural language AI model, Google, Baidu and others are working on competitors. Google’s LaMDA is convincing enough that one former researcher threw away his job with the search giant last year by claiming the chatbot is sentient. (The human tendency to project feelings and consciousness onto algorithms is a concept we’ll likely hear much about in the coming years.) Google has only released extremely constricted versions of its chatbot in a beta, presumably out of ethical concerns. With the genie out of the bottle, it will be interesting to see how long that restraint lasts.
