Kibsi raises $9.3M for its no-code computer vision platform
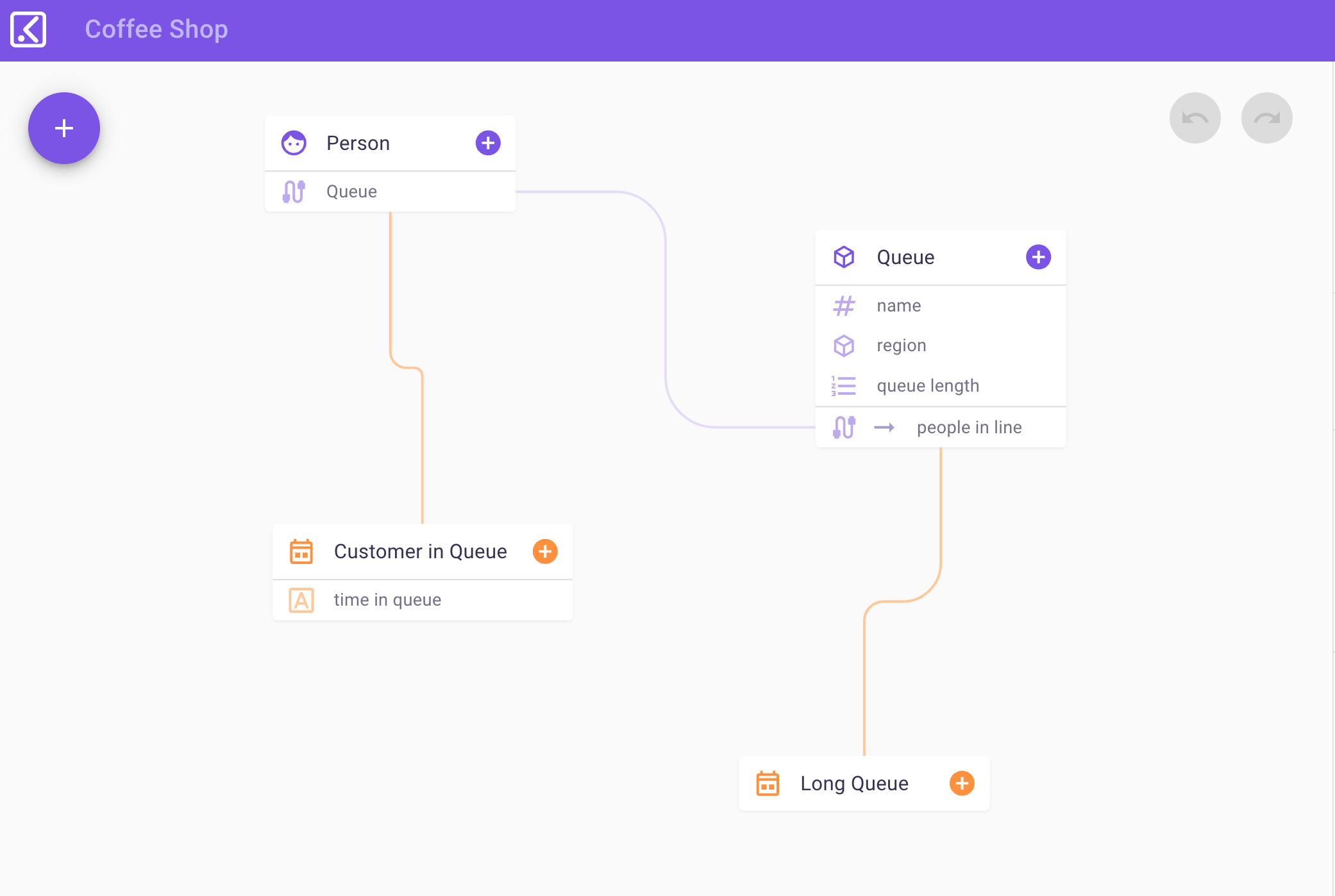
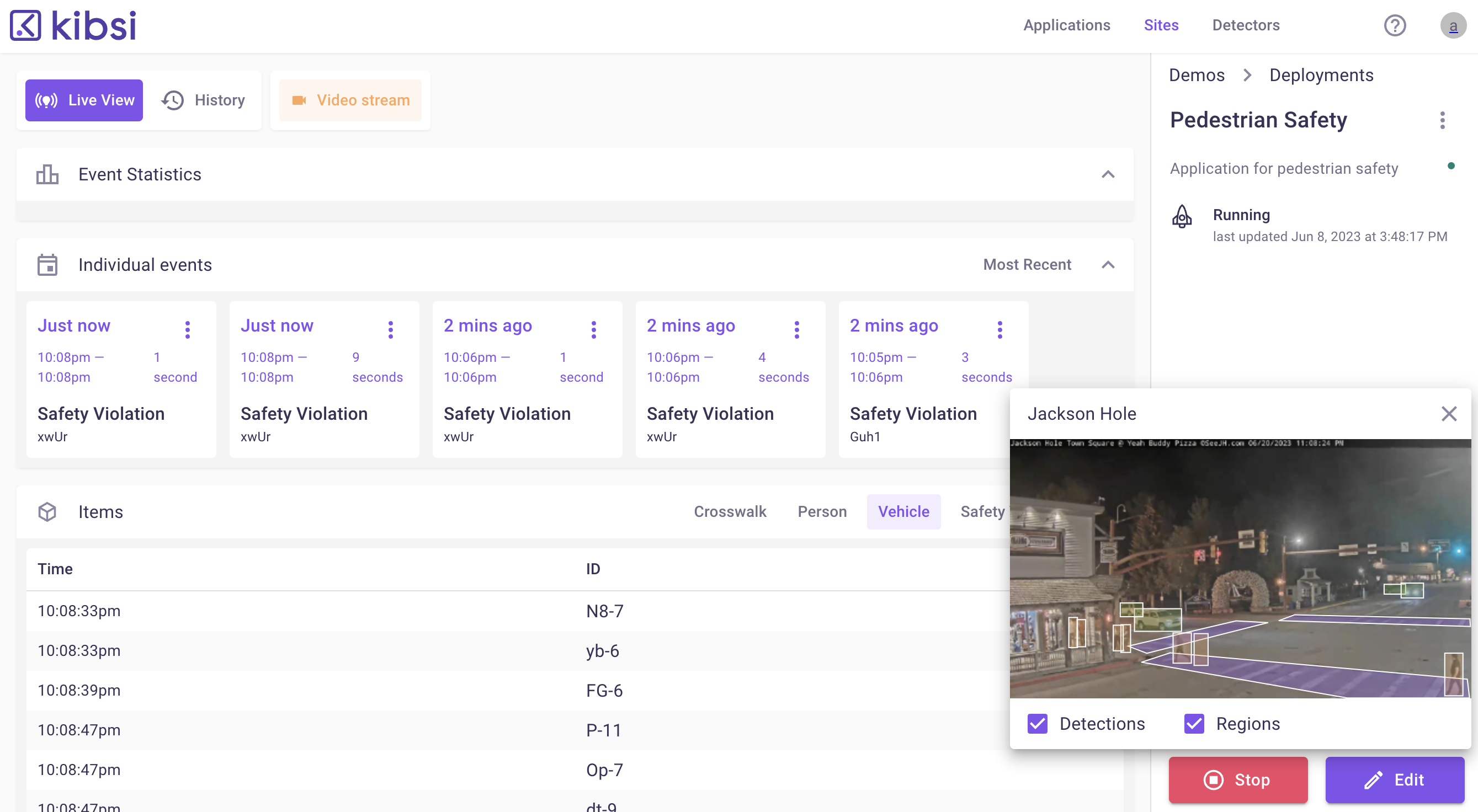
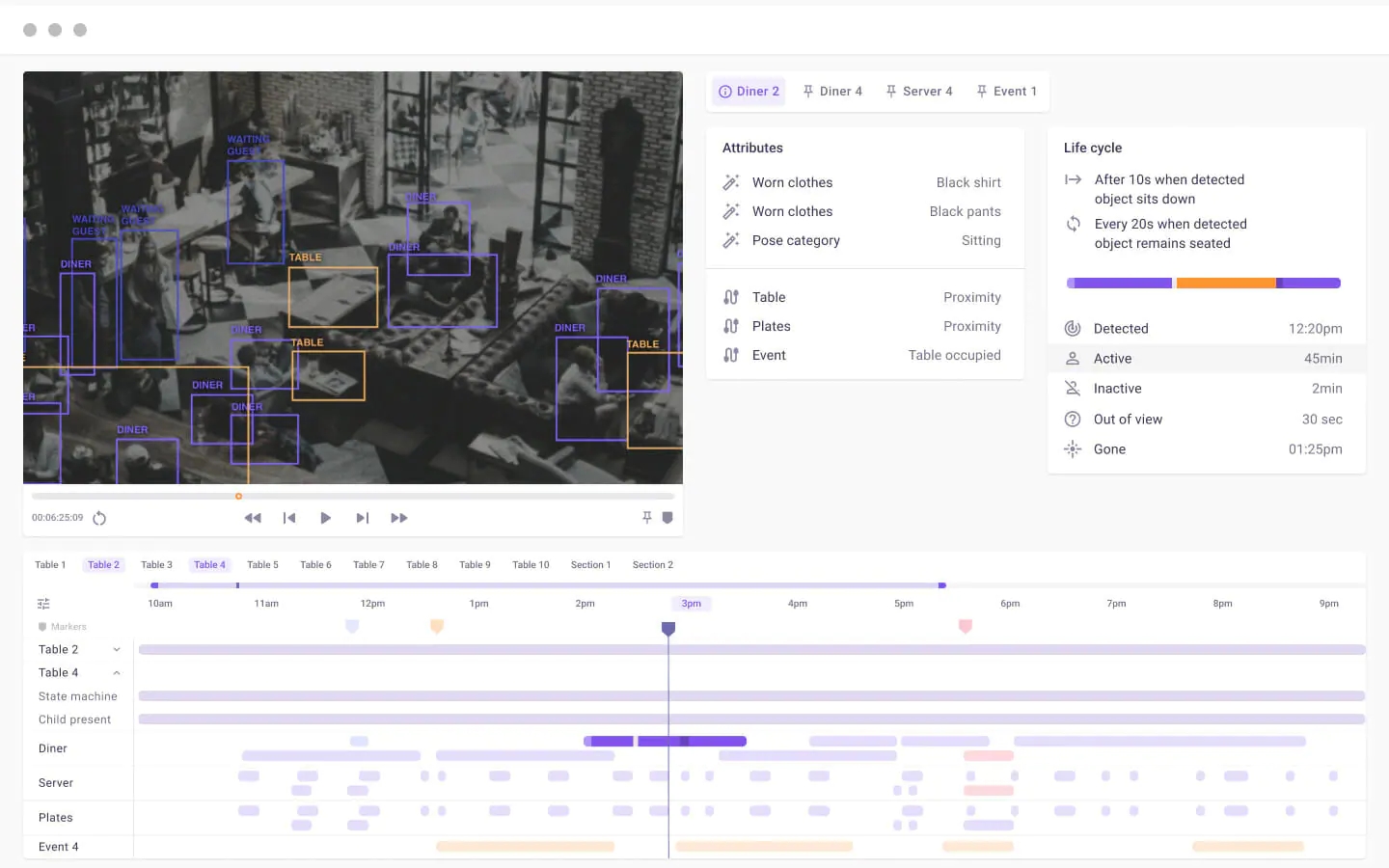
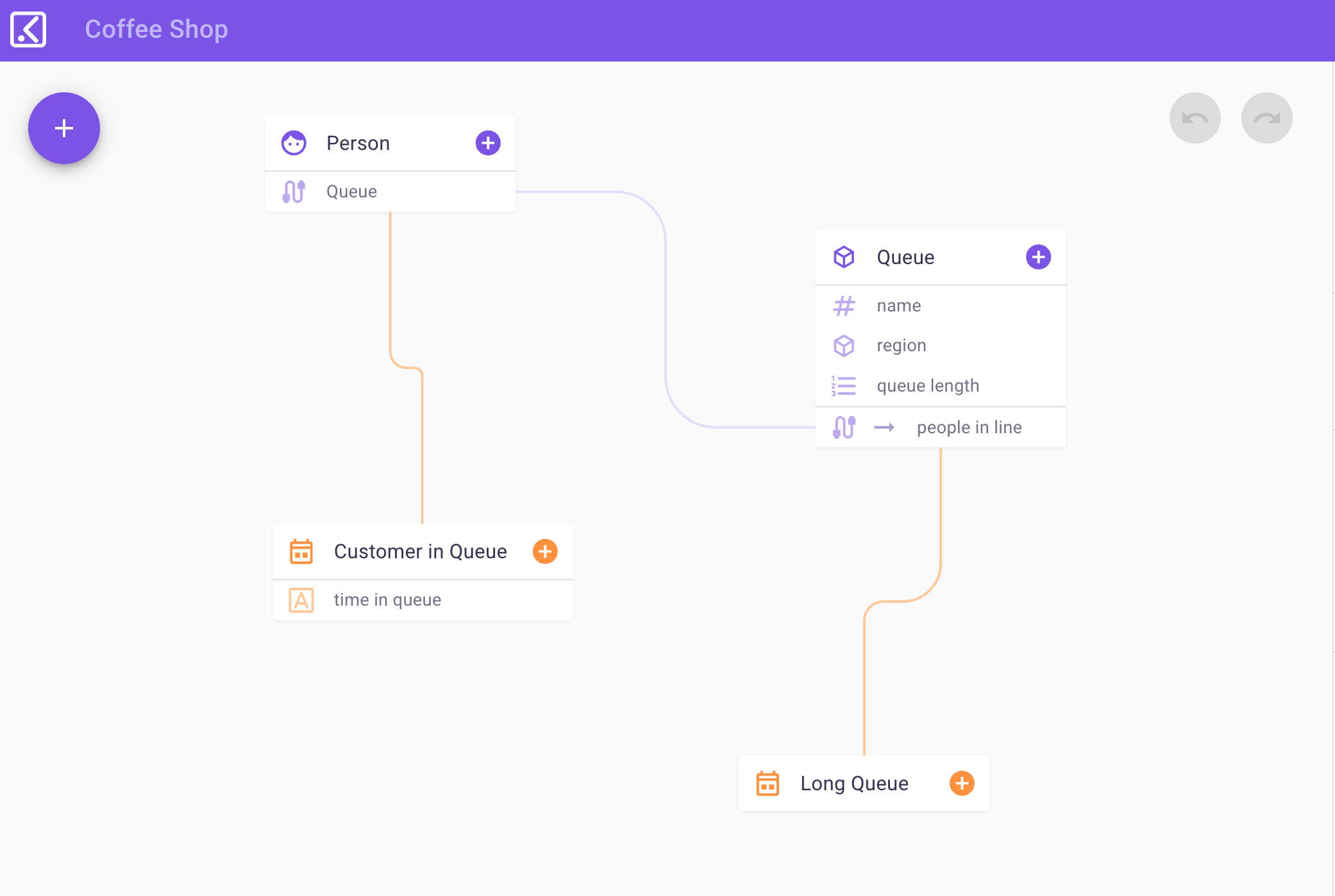
Kibsi is an Irvine, California-based startup that is building a no-code computer vision platform that allows businesses to build and deploy computer vision applications. Among the things that set Kibsi apart from many other players in this space is that it lets businesses reuse their existing cameras to create insights into virtually anything they want to track, be that in a warehouse, restaurant or on an airport ramp.
The company today announced that it has raised a total of $9.3 million in pre-seed and seed funding. The participants in these rounds were GTMfund, NTTVC (which led the $4 million pre-seed round), Preface Ventures, Ridge Ventures, Secure Octane, and Wipro Ventures.
Tolga Tarhan, who is now Kibsi’s CEO, joined Rackspace in 2019 after the founding team sold AWS-focused consulting business Onica to Rackspace. He later became the company’s CTO. After the Rackspace IPO, he decided that his journey in the company had come full circle. Together with co-founders and former Onica execs Amanda McQueen, Amir Kashani and Eric Miller, the team looked at what they could build next.
“I wanted to go get out and go create again,” Tarhan told me. “We wanted something that had an IoT orientation to it — because we’ve done a lot of IoT at Onica, was a big part of our business. We wanted it to be software — we had done enough consulting for multiple lifetimes. And we wanted it to be something involving AI, because we thought IoT by itself was almost old news. How do we combine these things? And as we thought about that space and our experience and where we got into roadblocks with customers, we realized that many customers are having trouble implementing computer vision.”
He noted that too often, computer vision projects in large enterprises fail even though they have the cameras and the talent to work on models. But to ingest stream from their cameras to then run the models takes a lot of undifferentiated work — and integrating all of this with downstream applications presents another set of integration challenges. So the team decided to build a computer vision platform that enables businesses to use their existing cameras and then combine that with a user experience that quickly enables users to gain real business value from this data. The platform lets users run their own computer vision models or Kibsi’s own and it then presents the results in a way that matches the business intent, both in Kibsi’s own user interface and through an API.
“We don’t return X and Y coordinates of people and objects,” said Tarhan. “If you’re thinking about a business analyst’s job, they don’t really care that a person is standing at this coordinate — what they want to know is: did that person interact with that merchandise?”
Kibsi has already attracted attention from customers like Owens Corning. Yet while manufacturing is a natural environment for computer vision, the Kibsi team also counts the likes of Whisker, which is embedding Kibsi’s tech into their litter robot, and the Woodland Park Zoo among its customers.
“Tracking animal behavior and interactions requires our professionals to sift through hours of
camera footage,” said Bonnie Baird, Animal Welfare Scientist at Woodland Park Zoo. “We are
excited to add Kibsi’s computer vision capabilities to our existing cameras to gain valuable
insights about our animals and their well-being.”
While there are also obvious use cases for Kibsi in the smart city space (and its investor NTT is a major player there), Tarhan noted that the sales cycles there are quite slow. “As a startup, it’s not the best place to play day one,” he said.
Kibsi offers a free trial of their platform for developers, with a more comprehensive developer plan starting at $99/month. For premium and enterprise pricing plans, potential customers need to contact the company directly.